| 일 | 월 | 화 | 수 | 목 | 금 | 토 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | ||||||
| 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
| 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 13 | 14 | 15 |
| 16 | 17 | 18 | 19 | 20 | 21 | 22 |
| 23 | 24 | 25 | 26 | 27 | 28 | 29 |
| 30 |
- 분리 집합
- Meet in the middle
- 누적 합
- DFS
- spring boot
- Java
- kapt
- MST
- miller-rabin
- concurreny
- MySQL
- SCC
- kruskal
- springdoc
- DP
- 투 포인터
- 백트래킹
- BindingAdapter
- Linux
- union-find
- 알고리즘
- 위상 정렬
- 그래프
- 이분 탐색
- disjoint set
- 구현
- 위상정렬
- 페르마 소정리
- tarjan
- BFS
- Today
- Total
기맹기 개발 블로그
[BOJ 1799] 비숍 (Java) 본문
BOJ 1799 비숍
난이도 : 골드 1
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1799
1799번: 비숍
첫째 줄에 체스판의 크기가 주어진다. 체스판의 크기는 10이하의 자연수이다. 둘째 줄부터 아래의 예와 같이 체스판의 각 칸에 비숍을 놓을 수 있는지 없는지에 대한 정보가 체스판 한 줄 단위로
www.acmicpc.net
전략
N-Queen를 백트래킹으로 풀 때와 유사하지만 다음 조건들이 다르다.
1. 놓을 수 없는 위치가 존재한다는 점
2. 놓을 수 있는 비숍의 최대 개수를 구해야한다는 점
3. 비숍은 자신이 속한 흑/백 칸이 아닌 곳으로는 이동할 수 없다는 점
흑색/백색 칸을 따로 dfs로 진행하면서 더 이상 비숍을 놓을 수 없는 경우에는 백트래킹하고,
놓을 수 있는 경우에는 비숍의 개수를 증가시키고 최댓값을 갱신시킨다.
시행착오
1. 매번 다음 인덱스를 찾기 위해 N^2만큼의 탐색을 진행하여 시간초과 (라고 생각했었음)
=> map이 1인 위치를 모두 ArrayList에 저장한 후에 다음 인덱스를 바로 찾도록-> O(1)로 줄임
2. 그래도 시간초과..
이것이 문제의 코드다..
map[i] == true 인 곳이 X이라고 하면 시간복잡도가 O(2^X)이다.
pruning이 된다고 해도 X는 최대 100까지 가능하므로, 알고리즘의 수정이 필요하다.
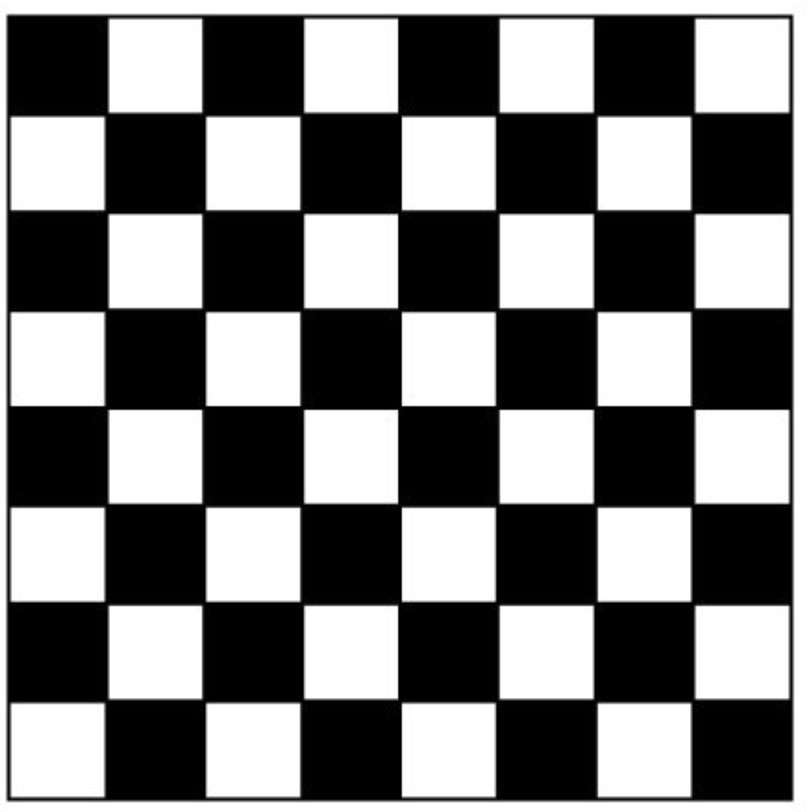
비숍은 대각선으로만 이동하므로 자신이 속한 색이 아닌 칸으로는 이동할 수 없다. 이 아이디어가 전략 3에 추가되고 시간복잡도를 줄일 해결법을 찾게 된다.
따라서 흑/백 칸에 대해서 따로 dfs를 진행하고 두 결과를 합치면 되는 것이다. 이렇게 개선하면 X가 절반으로 줄어들어서 해결할 수 있다.
코드
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static boolean[][] map;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new boolean[N][N];
int[][] placedBlack = new int[N][N];
int[][] placedWhite = new int[N][N];
ArrayList<Position> posBlack = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Position> posWhite = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) == 1;
if (map[i][j]) {
if ((i + j) % 2 == 0)
posBlack.add(new Position(i, j));
else
posWhite.add(new Position(i, j));
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
if (!posBlack.isEmpty())
ans += dfs(posBlack, placedBlack, 0, 0);
if (!posWhite.isEmpty())
ans += dfs(posWhite, placedWhite, 0, 0);
System.out.println(ans);
}
static int dfs(final ArrayList<Position> positions, final int[][] placed, int idx, int cnt) {
if (!(idx < positions.size())) return cnt;
int ret = 0;
Position cur = positions.get(idx);
if (placed[cur.y][cur.x] == 0) {
addPlace(placed, cur.y, cur.x, 1);
ret = Math.max(dfs(positions, placed, idx + 1, cnt + 1), ret);
addPlace(placed, cur.y, cur.x, -1);
}
ret = Math.max(dfs(positions, placed, idx + 1, cnt), ret);
return ret;
}
static void addPlace(final int[][] placed, int y, int x, int num) {
placed[y][x] += num;
for (int i = 1; y - i >= 0 && x + i < N; i++)
placed[y - i][x + i] += num;
for (int i = 1; y - i >= 0 && x - i >= 0; i++)
placed[y - i][x - i] += num;
for (int i = 1; y + i < N && x - i >= 0; i++)
placed[y + i][x - i] += num;
for (int i = 1; y + i < N && x + i < N; i++)
placed[y + i][x + i] += num;
}
static class Position {
int y;
int x;
Position(int y, int x) {
this.y = y;
this.x = x;
}
}
}위 코드는 비숍을 놓을 수 있는지 확인은 O(1), 놓는 것은 O(N)이 소모된다.
만약 모든 위치를 2차원 배열에 저장하지 않고, 각 대각선의 정보만 저장한다면 두 작업 모두 O(1)에 끝낼 수 있다.
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
public class Main {
static int N;
static boolean[][] map;
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
N = Integer.parseInt(br.readLine());
map = new boolean[N][N];
int[] diagDown = new int[2 * N - 1];
int[] diagUp = new int[2 * N - 1];
ArrayList<Position> posBlack = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Position> posWhite = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
StringTokenizer st = new StringTokenizer(br.readLine());
for (int j = 0; j < N; j++) {
map[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(st.nextToken()) == 1;
if (map[i][j]) {
if ((i + j) % 2 == 0)
posBlack.add(new Position(i, j));
else
posWhite.add(new Position(i, j));
}
}
}
int ans = 0;
if (!posBlack.isEmpty())
ans += dfs(posBlack, diagUp, diagDown, 0, 0);
if (!posWhite.isEmpty())
ans += dfs(posWhite, diagUp, diagDown, 0, 0);
System.out.println(ans);
}
static int dfs(final ArrayList<Position> positions, final int[] diagUp, final int[] diagDown, int idx, int cnt) {
if (!(idx < positions.size())) return cnt;
int ret = 0;
Position cur = positions.get(idx);
int diagUpIdx = cur.y - cur.x + N - 1;
int diagDownIdx = cur.y + cur.x;
if (diagUp[diagUpIdx] == 0 && diagDown[diagDownIdx] == 0) {
diagUp[diagUpIdx] += 1;
diagDown[diagDownIdx] += 1;
ret = Math.max(dfs(positions, diagUp, diagDown, idx + 1, cnt + 1), ret);
diagUp[diagUpIdx] -= 1;
diagDown[diagDownIdx] -= 1;
}
ret = Math.max(dfs(positions, diagUp, diagDown, idx + 1, cnt), ret);
return ret;
}
static class Position {
int y;
int x;
Position(int y, int x) {
this.y = y;
this.x = x;
}
}
}
깨달은 점
체스의 특성을 잘 생각해야 풀 수 있는 문제로 이런 아이디어를 떠올리는 것이 매우 어렵게 느껴졌다.
효율적인 문제해결 방법을 찾기 위해서는 내 코드만 고칠 것이 아니라 문제를 잘 생각해보아야 할 것 같다.
'PS' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [BOJ 10986] 나머지 합 (Java) (0) | 2022.08.20 |
|---|---|
| [BOJ 2143] 두 배열의 합 (Java) (0) | 2022.08.18 |
| [BOJ 1644] 소수의 연속합 (Java) (0) | 2022.08.17 |
| [BOJ 1806] 부분합 (Java) (0) | 2022.08.17 |
| [BOJ 14003] 가장 긴 증가하는 부분 수열 5 (Java) (0) | 2022.08.16 |
